autoBOTLib library¶
Next follows a minimal usecase, where you are introduced to basic autoBOTLib functionality. The data used in the example is accessible at: https://github.com/SkBlaz/autobot/tree/master/data
The minimal example is given next. Let’s first inspect how a model is trained.
import autoBOTLib
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
## Load example data frame
dataframe = pd.read_csv("../data/insults/train.tsv", sep="\t")
train_sequences = dataframe['text_a'].values.tolist()
train_targets = dataframe['label'].values
autoBOTLibObj = autoBOTLib.GAlearner(
train_sequences, # input sequences
train_targets, # target space
time_constraint=1, # time in hours
num_cpu="all", # number of CPUs to use
task_name="example test", # task identifier
scoring_metric = "f1", # sklearn-compatible scoring metric as the fitness.
hof_size=3, # size of the hall of fame
top_k_importances=25, # how many top features to output as final ranking
memory_storage=
"./memory", # tripled base for concept features (see ./examples folder)
representation_type="neurosymbolic") # or symbolic or neural or neurosymbolic (neurosymbolic includes doc2graph transformation which is in beta)
autoBOTLibObj.evolve(
nind=10, ## population size
crossover_proba=0.6, ## crossover rate
mutpb=0.4) ## mutation rate
The autoBOTLibObj object now contains a trained model, explanations and other relevant information. Let’s explore its capabilities next.
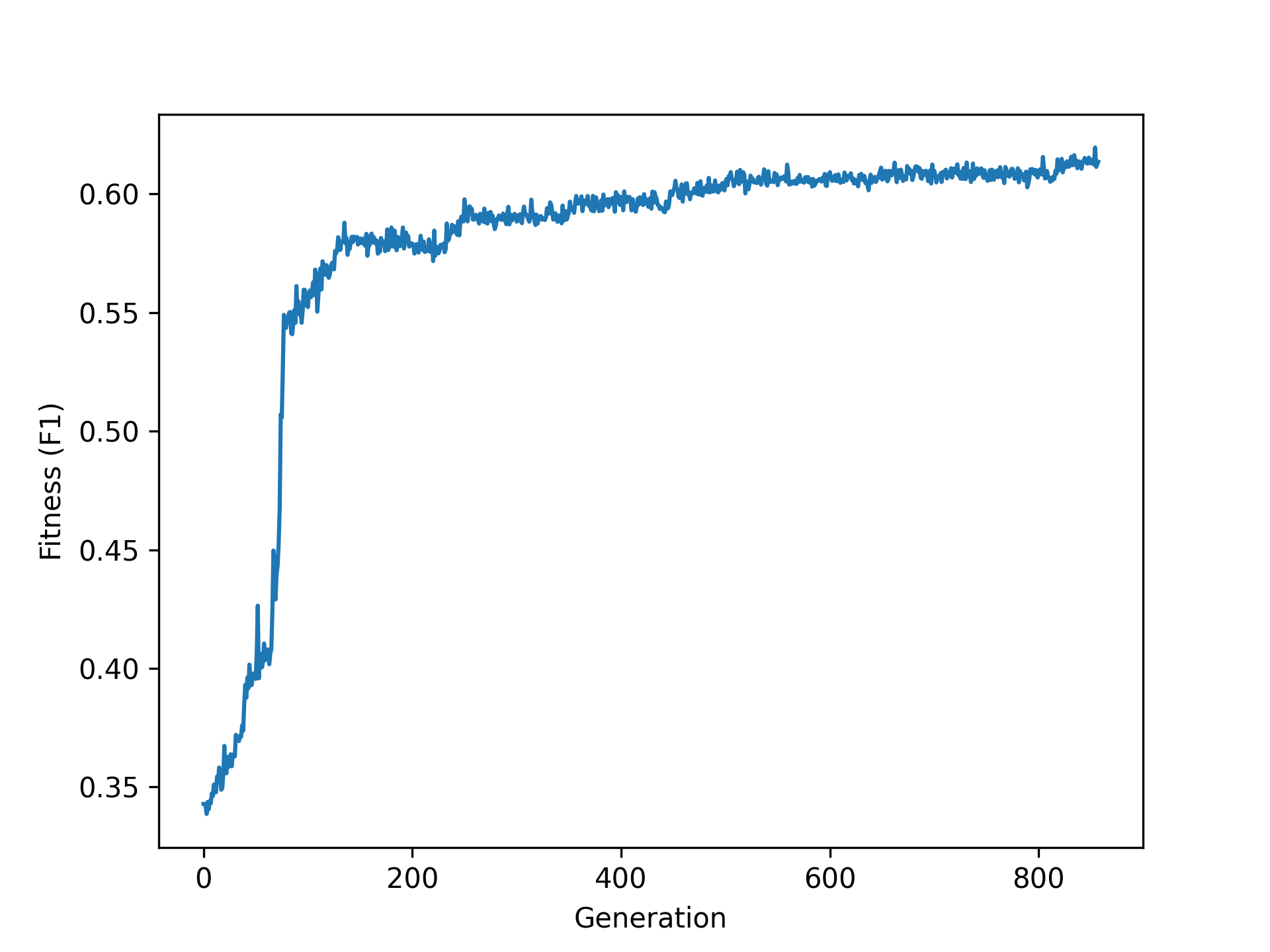
We can first visualize the evolution’s trace:
## visualize fitnesses
autoBOTLibObj.visualize_fitness(image_path = "fitness.png")
As autoBOTLib is fully explainable, we can explore the two layers of explanations as follows:
## store global importances
importances_local, importances_global = autoBOTLibObj.feature_type_importances()
print(importances_global)
Which results in subspace feature importances (importances_global):
Importance Feature subspace
0.4124583243111468 word_features
0.2811283792683306 char_features
0.27482709838903063 pos_features
1.0036820174140975 relational_features
0.5351954677290582 keyword_features
0.0 concept_features
0.4983623274641806 neural_features_dm
0.2565542438450016 neural_features_dbow
and the subspace-level rankings (importances_local):
keyword_features char_features word_features pos_features relational_features concept_features neural_features_dm neural_features_dbow
0 moron : 2.76 ck : 1.06 fake : 1.26 prp vbp dt : 3.42 o--3--d : 3.31 antonym(act,nothing) : 0.0 13_1 : 1.41 183_0 : 0.55
1 idiot : 2.62 fuc : 0.8 pig : 1.14 vbp dt : 2.99 n--15--s : 2.96 antonym(act,real) : 0.0 323_1 : 1.41 321_0 : 0.54
2 loser : 2.04 uck : 0.79 go back : 0.87 nn : 2.56 --3--c : 2.96 antonym(around,far) : 0.0 217_1 : 1.37 126_0 : 0.53
3 fa**ot : 1.99 f*ck : 0.77 azz : 0.58 prp vbp : 2.06 r--2--p : 2.84 antonym(ask,tell) : 0.0 414_1 : 1.26 337_0 : 0.52
4 ignorant : 1.57 fu : 0.69 jerk : 0.44 vbp dt jj : 2.0 u--2--s : 2.77 antonym(away,back) : 0.0 259_1 : 1.21 223_0 : 0.51
5 b*tch : 1.56 pi : 0.68 liar : 0.44 vbp dt nn : 1.74 n--6--g : 2.75 antonym(away,come) : 0.0 311_1 : 1.21 72_0 : 0.5
6 stupid : 1.49 gg : 0.66 stfu : 0.44 prp : 1.48 e--14--f : 2.74 antonym(away,stay) : 0.0 89_1 : 1.13 271_0 : 0.47
7 mouth : 1.47 uc : 0.65 ass ni**a : 0.39 vbp : 1.47 --10--t : 2.72 antonym(away,stay) relatedto(away,far) : 0.0 91_1 : 1.12 335_0 : 0.45
8 retarded : 1.39 u : 0.64 otr : 0.39 in : 1.44 c--4--g : 2.69 antonym(away,stay) relatedto(away,way) : 0.0 36_1 : 1.09 112_0 : 0.44
9 kidding : 1.21 dumb : 0.63 smug : 0.37 prp nn : 1.21 a--7--t : 2.68 antonym(bad,right) : 0.0 391_1 : 1.09 244_0 : 0.42
Finally, to explore the properties of individual classifiers in the final ensemble, you can obtain the table of results as:
final_learners = autoBOTLibObj.summarise_final_learners() print(final_learners)
Putting it all together - an automated report can be obtained as follows.
autoBOTLibObj.generate_report("report_folder")
For more examples and usecases, please inspect the examples folder!